As blockchain adoption accelerates, scalability is turning into one of many ecosystem’s most urgent challenges. With the expansion of decentralized purposes (dApps), sensible contracts, and better transaction volumes, blockchains should scale to deal with international demand. Two predominant approaches have emerged to deal with this: Layer-1 and Layer-2 scaling options.
Layer-1 (L1) refers back to the base protocol layer of a blockchain, equivalent to Bitcoin or Ethereum, whereas Layer-2 (L2) refers to protocols that function on prime of Layer-1 to reinforce throughput, scale back charges, and offload congestion. This information explores how each layers contribute to the way forward for blockchain infrastructure.
On this information:
- Layer-1 scaling options
- Resolving layer-1 limitations
- Layer-2 scaling options
- Varieties of layer-2 options
- What’s the blockchain trilemma?
- Layer-1 vs. layer-2: main variations
- The way forward for scaling
- Regularly requested questions
Layer-1 scaling options
Layer-1 (L1) scaling includes instantly bettering the bottom blockchain protocol to extend efficiency and capability. This might imply modifying consensus mechanisms, adjusting block sizes, or implementing new options like sharding. Key examples of L1 Blockchains embrace:
- Cardano, Solana, Avalanche: Compete as scalable Layer-1 networks with native design enhancements.
- Bitcoin: Optimized for decentralization and safety, however restricted in throughput.
- Ethereum: Transitioned from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to enhance scalability and vitality effectivity.

Layer-1 scaling options enhance the blockchain layer’s basis to facilitate scalability enhancements. This presents a variety of how to extend the scalability of blockchain networks.
Layer-1 options, as an example, can allow direct modifications to protocol guidelines to extend transaction capability and pace. Likewise, layer-1 scaling options can present higher capability for accommodating further knowledge and customers.
Layer-1 scaling strategies
- Block dimension and block time changes: Bigger blocks and shorter block intervals permit extra transactions per second (TPS), however can impression decentralization.
- Consensus mechanism upgrades: Transferring from PoW to PoS reduces vitality use and permits sooner finality.
- Sharding: Divides community state into smaller elements (“shards”) processed in parallel. Utilized by Ethereum 2.0, Zilliqa, Polkadot.
Benefits
- Scalability can be the obvious benefit of layer-1 blockchain options. Layer-1 blockchain options necessitate protocol modifications for enhanced scalability.
- A layer-1 blockchain protocol gives decentralization and safety with excessive scalability and financial viability.
- Layer-1 enhances ecosystem growth. In different phrases, layer-1 scaling options may incorporate new instruments, technological developments, and different variables into the bottom protocols.
Disadvantages
- Requires arduous forks or protocol upgrades
- Slower to deploy attributable to governance and coordination complexity
Resolving layer-1 limitations
Even with upgrades, Layer-1 blockchains face scalability ceilings. Bitcoin’s PoW mechanism limits throughput, and Ethereum confronted excessive fuel charges throughout congestion. Two notable options are:
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Replaces miners with validators who stake tokens. Utilized in Ethereum, Cardano, and Tezos.
- Sharding: Breaks the blockchain into parallel-processing shards. Ethereum 2.0 and Polkadot make the most of sharded designs to spice up throughput.
These approaches goal to deal with the blockchain trilemma: the trade-off between scalability, decentralization, and safety.
Enhancements to the consensus protocol
Some consensus mechanisms are extra environment friendly than others. PoW is right this moment’s consensus protocol on fashionable blockchain networks equivalent to Bitcoin. PoW is safe, however it may be sluggish. Consequently, PoS is the consensus mechanism of selection for many new blockchain networks. This is a vital issue within the layer-1 vs. layer-2 blockchain debate.
PoS methods don’t require miners to resolve encryption algorithms utilizing a whole lot of computing energy. As a substitute, community members use PoS to course of and confirm transaction blocks. Ethereum will transition to a PoS consensus algorithm, which is to extend the community’s capability whereas enhancing decentralization and preserving community safety.
Sharding
Tailored from distributed databases, sharding has grow to be some of the fashionable layer-1 scaling options. Sharding is the method of breaking apart the state of the entire blockchain community into separate units of information known as “shards.” A process that’s simpler to deal with than in search of all nodes to deal with the entire community.
The community processes these shards in parallel, permitting for the sequential processing of a number of transactions. As well as, every community node is assigned to a particular shard reasonably than sustaining an entire copy of the blockchain. Every shard sends proofs to the mainchain and shares addresses, common states, and balances with different shards utilizing cross-shard communication methods. Together with Zilliqa, Qtum, and Tezos, Ethereum 2.0 is a outstanding blockchain protocol at the moment investigating shards.
Layer-2 scaling options
Layer-2 (L2) refers to applied sciences constructed on prime of Layer-1 blockchains to enhance scalability with out altering the underlying protocol. They course of transactions off-chain and submit ultimate outcomes again to the bottom layer, relieving strain on the principle community.
The first goal of layer-2 scaling is to make use of networks or applied sciences that function on prime of a blockchain protocol. An off-chain protocol or community may assist a blockchain community obtain elevated scalability and effectivity.
Layer-2 scaling options facilitate the delegation of information processing duties in assist structure extra effectively and flexibly. Consequently, the core blockchain protocol doesn’t expertise congestion, making scalability attainable. Key examples of L2 protocols embrace:
- zkSync, Starknet: Use zk-rollups to batch 1000’s of transactions with cryptographic proofs.
- Lightning Community (Bitcoin): Permits near-instant micropayments through fee channels.
- Optimism & Arbitrum (Ethereum): Use optimistic rollups to scale Ethereum with out compromising safety.
Benefits
- One of the important benefits of a layer-2 answer is that it doesn’t have an effect on the efficiency or performance of the underlying blockchain to degrade the community’s general efficiency.
- Layer-2 options, equivalent to state channels and Lightning Community, expedite the execution of a number of micro-transactions. It is because it doesn’t endure minor verifications or pay pointless charges to conduct such transactions.
Disadvantages
- Layer-2 has a destructive impression on blockchain connectivity: One of the important points in blockchain proper now’s the dearth of interconnectivity between completely different blockchains (for instance, you can’t join with somebody on Ethereum if you’re on Bitcoin). It is a extremely problematic matter. With layer-2, it may possibly exacerbate this challenge by limiting interconnectivity inside a community, as layer-2 customers are restricted to the protocols of the options they make use of, which is turning into a problem.
- Privateness and questions of safety: As you’ll have noticed within the previous part, varied options supply various ranges of safety and privateness. Nevertheless, not one of the options gives the identical degree of safety as the key chains, so relying in your priorities, it’s best to give it some thought.
Varieties of layer-2 options
Nested blockchains, state channels, and sidechains are all examples of options for scaling on the layer-2 degree.
Rollups
Rollups batch transactions and submit them as a single proof to L1. The most well-liked rollup designs are Zero-Information (ZK) and optimistic rollups. Each take a unique method to securing the blockchain’s state.
A zk-rollup is a layer-2 scaling answer that batches transactions off-chain and makes use of zero-knowledge proofs to confirm their validity on-chain, guaranteeing excessive safety and quick finality with minimal knowledge posted to the bottom layer.
An optimistic rollup, in contrast, assumes transactions are legitimate by default and solely verifies them if somebody submits a fraud proof throughout a problem interval. The important thing distinction lies in verification: zk-rollups show correctness upfront utilizing cryptographic proofs, whereas optimistic rollups depend on financial incentives and a delay window for fraud detection.
Nested blockchains
Basically, a nested blockchain is a blockchain inside, or reasonably, on prime of, one other blockchain. The nested blockchain sometimes contains a main blockchain that establishes parameters for a extra intensive community, with executions occurring inside an interconnected community of secondary chains.
On prime of a mainchain, many blockchain tiers may be constructed, every with its personal parent-child connection. The father or mother chain delegates duties to baby chains, which then full them and returns the outcomes to the father or mother.
Until there’s a want for dispute decision, base blockchain doesn’t take part within the community capabilities of subsidiary chains. This mannequin’s work distribution reduces the processing load on the mainchain, which exponentially improves scalability. The OMG Plasma mission illustrates layer-2 nested blockchain infrastructure, which is used on prime of the layer-1 Ethereum protocol.
State channels
A state channel permits bidirectional communication between a blockchain and off-chain transactional channels, enhancing transactional capability and pace. A state channel doesn’t trigger validation by layer-1 community nodes. Somewhat, it’s a network-adjacent useful resource remoted through multi-signature or sensible contract mechanisms.
When transactions are finalized on a state channel, a ultimate “state” of the channel and its adjustments are written on the underlying blockchain. State channels embrace Liquid Community, Ethereum’s Raiden Community, Celer, and Bitcoin Lightning. In a trilemma tradeoff, the state channels quit a portion of their decentralization for higher scalability.
Sidechains
A sidechain is a transactional chain adjoining to a blockchain, sometimes used for bulk transactions. Sidechains use a consensus mechanism unbiased of the principle chain, and customers can optimize them for pace and scalability. The first perform of the principle chain in a sidechain structure is to keep up general safety, validate batched transaction data, and resolve disputes.
Sidechains are completely different from state channels in a number of elementary methods. First, sidechain transactions will not be non-public between members; they’re recorded publicly on the blockchain. Moreover, sidechain safety breaches don’t have an effect on the principle chain or different sidechains. The infrastructure of a sidechain is usually constructed from the bottom up, so establishing one may require important effort.
What’s the blockchain trilemma?
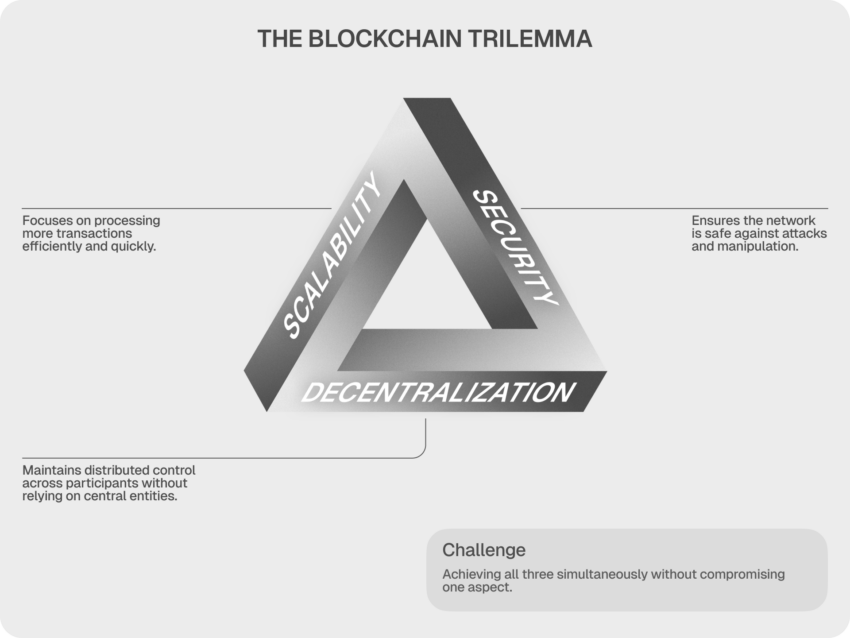
The scalability trilemma refers to a blockchain’s potential to stability three natural properties that represent its core rules: safety, decentralization, and scalability.
The trilemma states that a blockchain can solely possess two of the three properties, by no means all three concurrently. Consequently, the present blockchain expertise will all the time have to sacrifice considered one of its elementary properties for its performance. Bitcoin is a chief instance of this; whereas its blockchain has optimized decentralization and safety, it has supplied scalability.
Most significantly, no cryptocurrency is at the moment able to reaching the utmost of all three options. In different phrases, cryptocurrencies prioritize two or three options to the detriment of the remaining one.
Many builders are diligently working to resolve the blockchain trilemma, with some strategies and concepts already carried out that goal to resolve the scalability drawback. Relying on their degree of blockchain implementation, these ideas and strategies manifest as both layer-1 or layer-2 options.
A variety of blockchains can course of 1000’s of transactions per second, however they accomplish that on the expense of decentralization or safety. Most blockchains right this moment sacrifice one:
- Ethereum goals to stability all three through layer-2 rollups and sharded PoS.
- Bitcoin maximizes safety and decentralization on the expense of scalability.
- Solana prioritizes scalability and efficiency however reduces decentralization.
No blockchain has totally solved the trilemma, however improvements at each Layer-1 and Layer-2 proceed to push boundaries.
Layer-1 vs. layer-2: main variations
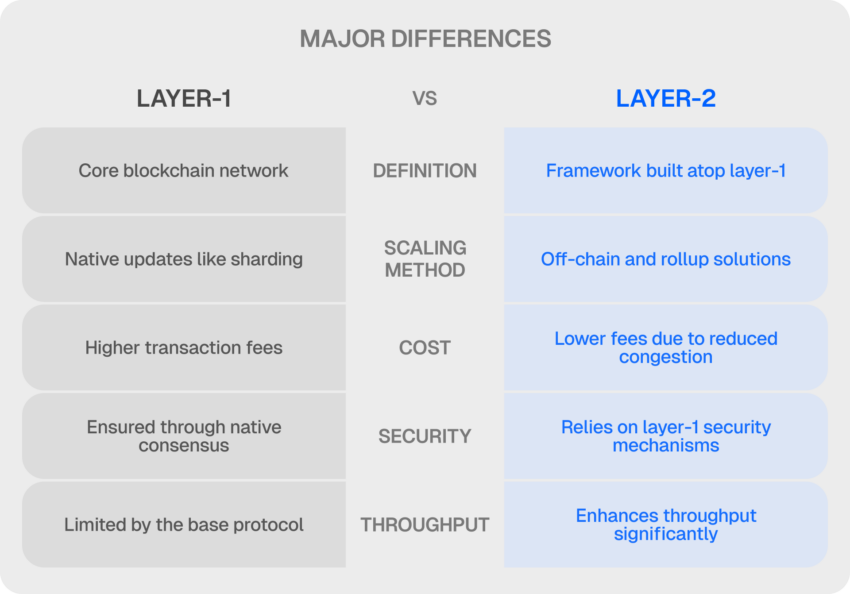
The elemental define of layer-1 and layer-2 scaling options gives the correct foundation for distinguishing between them. Listed here are among the key distinctions between layer-1 and layer-2 scaling options for blockchains.
1. Definition
Layer-1 scaling options modify the blockchain protocol’s base layer to realize the specified enhancements. As an example, the block dimension can modify to accommodate extra transactions, or customers can alter the consensus protocols to enhance pace and effectivity.
Layer-2 scaling options perform as off-chain options that share the load of the first blockchain protocol. Particular data processing and transaction processing duties are delegated to layer-2 protocols, networks, or purposes by the mainnet of a blockchain protocol. The off-chain protocols or options full the designated process and report the end result to the principle blockchain layer.
2. Technique of operation
With layer-1 blockchain networks, the precise scaling technique focuses on modifying the core protocol. With layer-1 scaling options, you have to change blockchain protocols. Subsequently, you wouldn’t be capable to instantly reduce the modifications if the transaction quantity drastically decreases.
In distinction, layer-2 scaling options perform as off-chain options that function independently of the first blockchain protocol. Off-chain protocols, networks, and options report solely the final word outcomes required by the speedy blockchain protocol.
3. Varieties of options
Within the case of layer-1 blockchain options, consensus protocol enhancement and sharding are two outstanding varieties of options. Scaling of layer-1 consists of alterations to dam dimension or block creation pace to make sure the specified performance.
Concerning blockchain layer-2 scaling options, there may be nearly no restriction on the options that may be carried out. Any protocol, community, or software could be a layer-2 answer off-chain for blockchain networks.
4. High quality
Layer-1 networks function the definitive supply of knowledge and are in the end accountable for transaction settlement. On layer-1 networks, a local token is used to entry the community’s assets. One other important attribute of layer-1 blockchain networks is innovation in consensus mechanism design.
Layer-2 networks present the identical performance as layer-1 blockchains, plus further traits. For instance, layer-2 networks enhance throughput and programmability while decreasing transaction prices. Every layer-2 answer has its personal technique for remapping transactions to their respective base layer.
The way forward for scaling
Layer-1 and Layer-2 options each play important roles in scaling blockchain networks. Layer-1 focuses on foundational integrity and protocol-level adjustments, whereas Layer-2 delivers sensible scalability enhancements with out burdening the bottom chain.
Understanding how these layers work together is vital to evaluating fashionable blockchain ecosystems, whether or not you’re a developer constructing purposes or an investor assessing scalability roadmaps.















