A ruble-backed stablecoin linked to sanctioned Russian monetary networks processed greater than $100 billion in onchain transactions in lower than a yr, in line with a brand new report from blockchain analytics agency Elliptic.
In a report revealed Thursday, Elliptic stated the A7A5 stablecoin was designed to function inside a broader framework meant to scale back publicity to Western monetary sanctions. The construction allowed Russian-linked companies to maneuver worth by crypto markets whereas limiting the danger of asset freezes.
Elliptic discovered that A7A5’s exercise surged following its launch in early 2025, earlier than slowing down within the second half of the yr as sanctions and compliance actions taken by exchanges and token issuers began to limit its usability.
Elliptic stated the size and construction of the flows spotlight how non-US greenback stablecoins will be designed to assist sanctioned commerce and the way enforcement strain can nonetheless disrupt such methods.
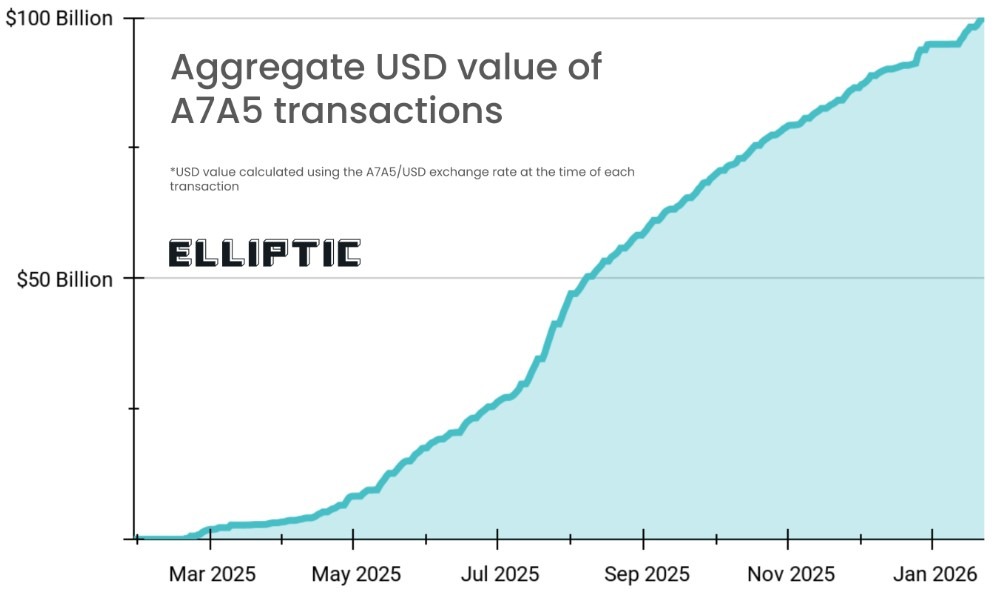
Mixture USD worth of A7A5 transactions. Supply: Elliptic
A7A5’s $100 billion determine and its function as a USDT bridge
Elliptic stated the $100 billion determine represents the cumulative worth of all A7A5 transfers recorded on public blockchains, together with Ethereum and Tron.
“That is the combination worth of all A7A5 transfers,” Tom Robinson, the founder and chief scientist at Elliptic, advised Cointelegraph.
“We aren’t taking a subjective view on whether or not every transaction constitutes distinct financial exercise, though the truth that transaction charges have been paid for all A7A5 transfers suggests all of them confer a profit to the transactor.”
Elliptic’s evaluation reveals that A7A5 has primarily functioned as a bridging asset between rubles and Tether’s USDt (USDT), which stays the most important dollar-pegged stablecoin globally.
The corporate stated the construction allowed customers to maneuver worth into USDT markets with out sustaining extended publicity to wallets weak to freezes by Western authorities.
The report famous that the stablecoin’s buying and selling exercise had been targeting a restricted variety of venues, together with Kyrgyzstan-based exchanges and project-linked infrastructure. This reinforces the token’s function as a purpose-built settlement software fairly than a broadly adopted retail stablecoin.
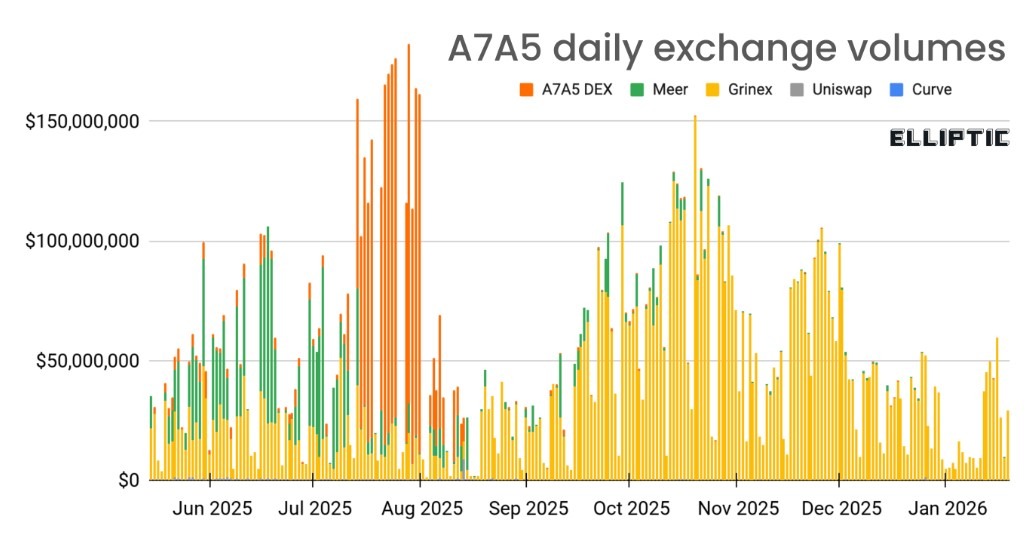
A7A5 each day change volumes. Supply: Elliptic
Associated: World sanctions linked to file flows into illicit crypto addresses
Sanctions strain and change controls curb progress
Elliptic stated the stablecoin’s enlargement slowed round mid-2025, with no main issuances since July and transaction volumes falling from peaks of $1.5 billion to about $500 million.
Robinson advised Cointelegraph that US sanctions imposed in August 2025 had probably the most quick and materials influence on the stablecoin’s performance.
“The US sanctions in August 2025 seem to have had the most important influence,” Robinson stated. “Instantly after the US designations, USDT liquidity provision to A7A5’s DEX dropped considerably, eradicating one of many stablecoin’s key advantages — simple on-chain entry to USDT.”
Further constraints adopted as exchanges software motion. In November 2025, decentralized change (DEX) Uniswap added A7A5 to its token blocklist, stopping buying and selling through its internet interface.
Elliptic additionally cited stories from customers whose USDT deposits had been frozen by exchanges after being traced again to A7A5-linked wallets.
On Oct. 23, the European Union formally sanctioned A7A5, describing it as a software used to bypass monetary restrictions tied to Russia’s warfare economic system.
Robinson stated A7A5’s trajectory illustrates each the potential and the boundaries of non-dollar stablecoins constructed for sanctions-era finance.
“Whereas the US greenback dominates the worldwide economic system, there are structural limits to how far a stablecoin corresponding to this will develop,” he advised Cointelegraph. “Nonetheless, if that modifications, all bets are off.”
Journal: How crypto legal guidelines modified in 2025 — and the way they’ll change in 2026















